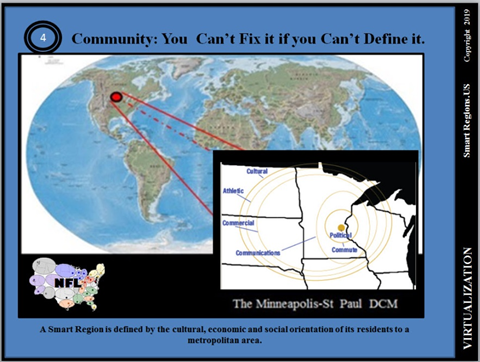
The Distributed City Model (DCM) is defined as that geographic area which is socio-economically oriented to a major metropolitan area. The five-state Minneapolis-St Paul DCM’s dynamic border reflects the relative strength of competing metro areas with a boundary roughly defined by the dominant market territories of cultural, athletic and business sales terri-tories. The DCM reflects a transformational opportunity presented to society by the distribu-tive nature of telecommunication technologies and the Suite of Telecommuting Applications (SoTA).
The goal of the DCM concept is to provide equity of opportunity, community viability and a higher quality of life throughout the DCM; it provides an alternative to the centralization forces of the Industrial Age and seeks to achieve a critical marketing level to support traditionally ur-ban services throughout the rural areas as well.
Sustaining Small Town America.
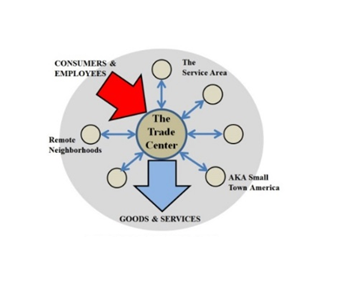
It is unfortunate but for many small towns, independent economic viability is no longer an option but preserving their sense of community remains- if they choose to collaborate with their trade center partner. Today, small towns provide employ-ees and consumers for the trade centers which reciprocate with little or no outreach; a more eq-uitable relationship is critical.
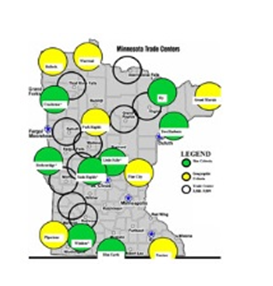
Creating a critical mass.
Rural trade centers are generally viable but much of their success is due to the resources they have drawn from their surrounding small towns, i.e., their “remote neighborhoods”. Broadband is particularly problematic as government has divided the market by creating their private system. The private sector has focused on the larger private users. The community demand is thereby so reduced that it can only be supported by subsidies. A differ-ent model is required.
The Global Context.
Most metropolitan regions are politically defined as a cluster of counties with no accountability its broader trade area as defined by the Distributed City Model. From a global perspective, The DCM’s broader definition with a homogeneous regulatory environment would be more competitive, would address the border community conflicts and generally would be more balanced for its communities and citizens.
The Distributed City Components-
Just as the Workforce Virtualization Program requires an infrastructure if it is to achieve its full potential, so too does the Distributed City Model. There are three components: leadership, technology and transportation.
1.LEADERSHIP-The Community Alliance (CA)
The CA provides leadership and management while serving as a catalyst for the commu-nity training programs, entrepreneurial outreach and community education. It coordinates the availability and delivery of all virtual content supporting the communities throughout the DCM.
The Alliance of each Community TeleCenter would have representation on the DCM’s regional management board and each small town would have representation on their re-spective TeleCenter partner. The organizational structure of this multi-level structure is critical to establish equity and balance throughout the DCM.
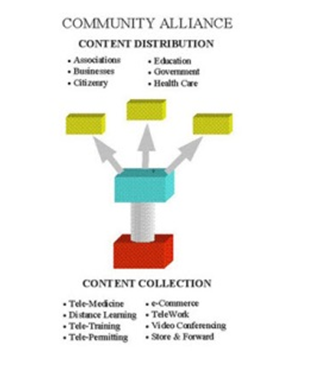
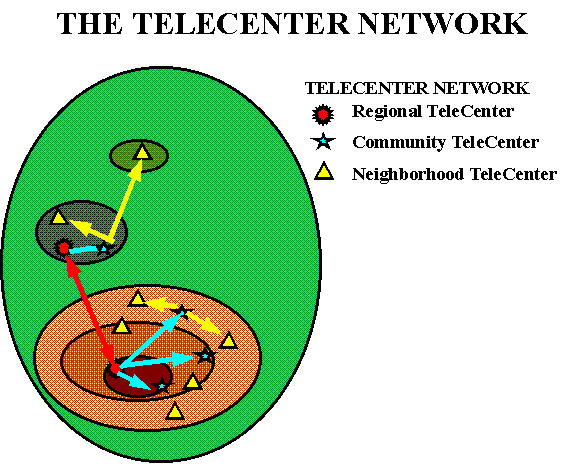
2. TECHNOLOGY- The Community TeleCenter Network (CTN)
Focuses on developing the critical mass of demand to make the Suite of Telecommuting Applications are affordable and universally available throughout the Smart Region. It consists of three networked TeleCenter types:
- Community– provides broadband switching and distribution, technology and com-munity support services; it is the community hub.
- Neighborhood– provides all regional services to the small towns and neighborhoods via its Community TeleCenter trade partner
- Regional– provides the tech training and support services to all Community Tele-Center staff
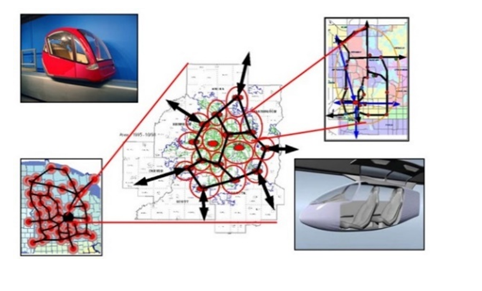
3. TRANSPORTATION- The Regional Transit Network (RTN)
While providing reliable commuting access to the urban areas, the RTN also provides an incredibly fast delivery / freight capability and, depending upon vehicle configuration, a tourism stimulus for the thousands of festivals and celebrations throughout the Smart Re-gion- great outings for our seniors! Only Personal Rapid Transit can affordably reach the sub centers within the DCM.