This article compares the dominant ad hoc approach to TCR’s strategic approach based upon the perspectives of the employer and the region. While there are other considerations, this list represents the most import concerns.
The Key: Ad Hoc– refers to the typical, government-sponsored, employee-benefit approach
Strategic – refers to the Workforce Virtualization Program’s managerial deployment approach
The Employer Perspective
CONSIDERATION (Employer) | THE AD HOC | THE STRATEGIC |
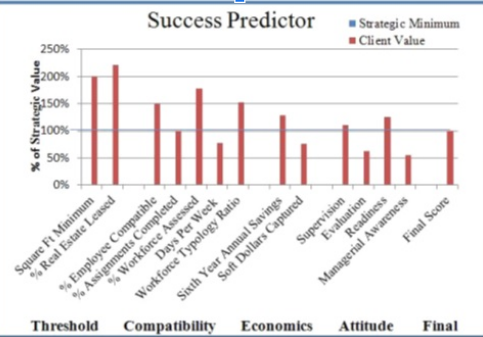
1. Fiscal Impact | ROI based upon soft dollar savings; no tools to determine costs. Many workers work remotely vastly less than the 2-3 days per week required to gain hard dollar savings | Initial Feasibility Analysis (FA) determines potential hard and soft dollar savings based upon regional values. Modeling process calculates savings based upon client values, deployment plan verifies and track s projected savings |
2. Program Expectations | Supports Work-Family balance | Fiscal and Operational benefits. After the FA is completed a workshop with senior staff is convened to setup guidelines for selecting the program’s optimum deployment plan and performance targets |
3. Plan Optimization |
n/a | Using sets of scenarios for provisioning, deployment, economics, TDM etc., a modeling screen is provided to generate projected results. The set of scenarios that best meets the Goals and Guidelines is adopted as the Master Scenario |
4. Facility “Right-Sizing” | Random people, working random schedules from random places makes this almost impossible | The Deployment Team converts the Master Scenario into one or more Deployment Cycles which defines the Plan’s schedule andsupports a sequential redesign / conversion of the facilities to reduce space |
5. Program Viability | Without a strong IT commitment, small programs are less effective; without a strong database to support large programs, they fail | Integrated plan development and implementation software supports the program and provides all of the assessments, calculation etc. |
1. Program Viability | Without a strong IT commitment, small programs are less effective; without a strong database to support large programs, they fail | Integrated plan development and implementation software supports the program and provides all of the assessments, calculation etc. |
2. Growth Potential | The pilot establishes a process for organic growth;generally no timetable or plan targets is prepared. | Barrier Mitigation process defines maximum deployment potential; the Workforce Virtualization Program builds the Plan to meet goals |
3. Continuity / Disaster Recovery Plan | Unclear how this can be accomplished without a scheduled deployment and system support | · Vulnerability Audit plots risk areas and potential COOP worker locations to ensure key people not in same risk zone as their office · Teams designed to support each corporate function · Deployed workforce offers recovery in minutes/hours not weeks |
4. Policy Focus | Mostly administrative | Comprehensive set of implementation policy to fulfill the plan’s goals. Some policies are universal; others are occupational or individually specific. Policy criteria developed for each job class and edited for each employee |
5. Telework Agreements | Typically a manual process | Computer generated with their provisioning equipment, custody signatures, work schedules, COOP roles etc. and backed by the Home Office Guidelines manual |
6. Program Tracking | Incompatible statistics or anecdotal summary of survey results | · Employees tied to Job Class which is tied to Occupation which is tied to U.S. Standard Occupational Classification which allows tracking across employers / industries · statistical component provides automated reporting at multiple levels |
7. Track Record | Yahoo, Best Buy, IBM and others have terminated their program- not tied to business objectives / no accountabilitycomponent | The Workforce Virtualization Program (WVP) institutionalizes telework by linking it to business objectives; it provides the tools to manage and refine the program, |
8. The Pilot | Select employees are trained for remote work | Tests the deployment and provisioning processes and all configuration combinations prior to full deployment |
9. Staffing | Voluntary with assessment | Nominated, Assessed, Reviewed,staff is deployed based upon occupational targets and COOP needs |
10. Worker Typology | Generally not addressed | This is foundational for deployingstaff and a key to statistical tracking trip generation etc. This plus “days per Week” are critical factors |
11. Provisioning | A variety of methods are used | Provisioning and Continuity Configurations are assigned to each job class to uniquely support their needs with products and services. The system tracks all products for easy maintenance or replacement |
12. Training | Various methods | Based upon the results of the FA, the training program is designed to meet the needs of the various audiences, i.e. teleworkers, family members, co-workers, managers etc. |
13. Barrier Mitigation | unknown | The Feasibility Analysis identifies various policy and operational barriers to a broader deployment, and provides a cost-effective analysis for each potential solution to determine the maximum possible deployment. |
The Regional Perspective
CONSIDERATION (Region) | THE AD HOC | THE STRATEGIC |
1. Crisis Management | n/a | Establishes multiple deployment schedules based upon regional risk levels that can activate greater deployment levels when needed |
2. Regional Infrastructure Demands, EnvironmentalTrends & Projections | n/a | Each year an abstract of each employer’s deployment status is generated, including protected staff profiles, and forwarded for analysis |
3. Congestion | With unscheduled workers, these numbers are often generated by a voluntary trip log | · With embedded GIS capabilities, special congestion relief tools can be used during road failures, reconstruction or any other reason · Encourages metro-wide analysis to capture potential from employees traveling to outside employers |
4. Conceptual Scope | Focus is only on telework | The Regional Virtualization Action Plan (RVAP) is a four-phase program that includes an analysis on other applications i.e., telemedicine, distance learning etc. and fosters a community engagement on whether virtual applications should be expanded and if so, how to facilitate those results |
5. Growth Potential | Anecdotal projections | The RVAP analyses the regional occupational base to project deployment potential, identify best occupations/industries and make numerous extrapolations for trips, CO2, etc. |
6. Support | In –person consultation | Data field descriptions on every form, PDFs for every phase, group sessions at key points and video support on demand |